What Are The Prevention Tips for Diabetes Type 1 And 2
- Diabetes is when your blood sugar is too high. Blood sugar or glucose is the primary sugar in your blood and provides energy to the body.
- Pre-diabetes is when the amount of sugar in the blood is above normal yet not high enough to be termed diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes is when the body no longer makes or does not have enough insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes develops when the pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin over time and blood sugar levels increase, such as after meals.
- People who are overweight and having the condition of obesity are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes is developed in case of pregnancy. Pregnant women make hormones that can lead to insulin resistance.
- However, gestational diabetes often goes away after the baby is born.
- The best tip to take care of your health is to consult your doctor to maintain blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
- Whenever you consult your physician, you must ask questions and accordingly prepare a list of questions before your visit.
- Do the following four things each day to maintain your blood glucose levels and stay in your target range:
- Follow your healthy eating plan.
- Be physically active.
- Take your medicines as prescribed.
- Monitor your diabetes.
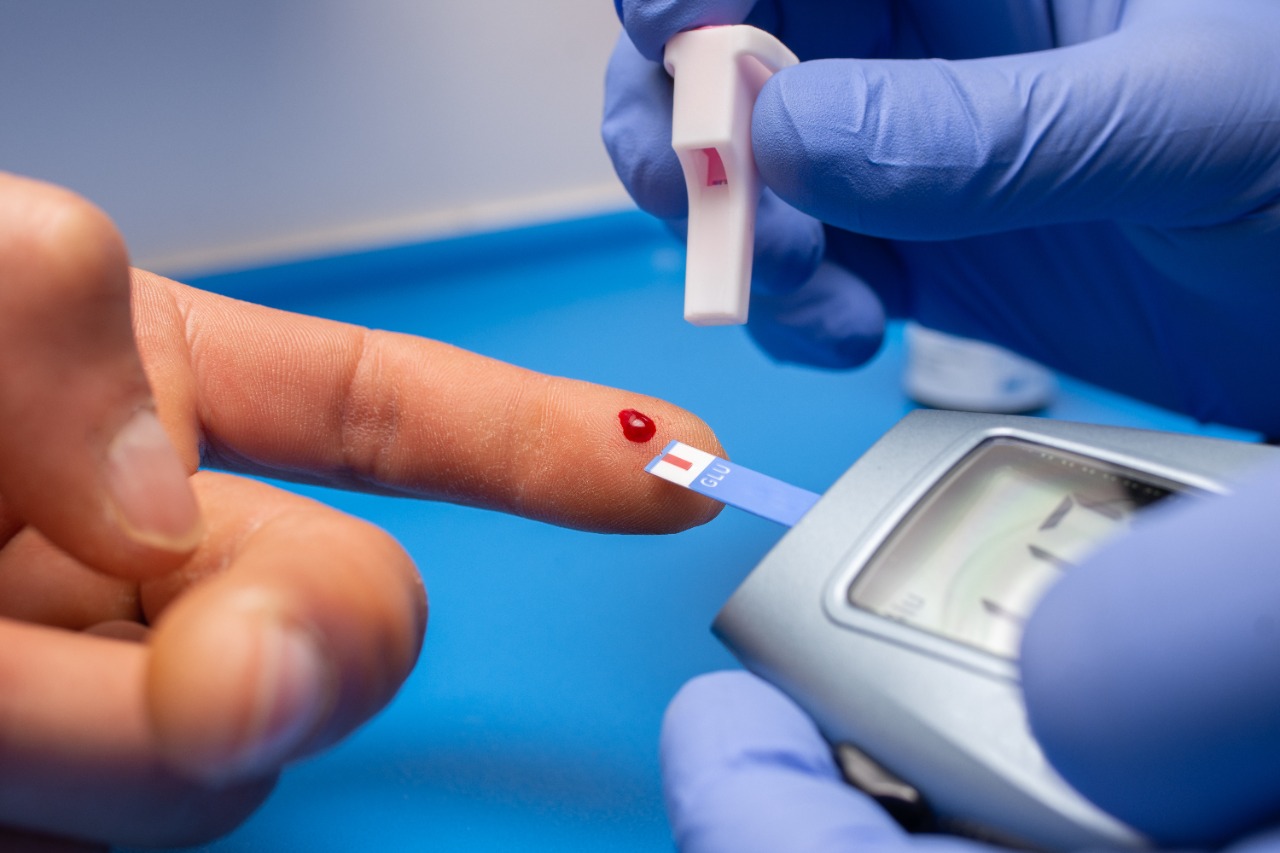
Image source: herminahospitals.com
- Discuss with your doctor regarding a dietitian who will prepare your food chart.
- Those with diabetes should do 30 to 60 minutes of activity most days of the week, while children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes should do 60 minutes of exercise every day.
- See your doctor before becoming physically active.
- Check your blood sugar levels before, during, and after physical activity.
- The Doctor prescribes diabetes medicines that work best for you and your lifestyle.
- If you have type 1 diabetes, you need insulin shots if your body has stopped making or doesn’t make enough. Some people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes also need to take insulin shots.
- Ask your healthcare team when you should take your diabetes medicines.
- Be sure to tell your doctor if your medicines make you feel sick or have other problems.
- Checking and recording your blood glucose levels can help you monitor and better manage your diabetes. Ask your doctor how often you should check your blood glucose levels.
- You may need to check your blood or urine for ketones if you’re sick or your blood glucose levels are above 240.
- Bring your blood glucose records to all visits with your healthcare team.
- If your blood glucose levels stay above 180 for more than 1 to 2 hours, they may be too high. High blood glucose and hyperglycemia mean you don’t have enough insulin.
- If your blood glucose levels drop below 70, you have low blood glucose, also called hypoglycemia.
- If you take diabetes medicines that can cause low blood glucose, always carry food for emergencies.
- If you take insulin, keep a prescription glucagon kit at home and at other places where you often go. If you have severe hypoglycemia, you’ll need someone to help bring your blood glucose levels back to normal by giving you a glucagon shot.
- How to prevent diabetes problems:
- Follow your healthy eating plan every day.
- Be physically active every day.
- Take your medicines every day.
- Check your blood glucose levels every day.
- You should have a plan for managing your diabetes when sick. You should call your doctor if you have questions about taking care of yourself.
- Tell your teachers, friends and peer groups that you have diabetes and teach them about the symptoms of low blood glucose. You may need their help if your blood glucose levels drop too low.
- Better to take your vaccines before you travel. Find out what shot you need for where you’re going, and ensure you get the right shots on time.
- When travelling, you must carry your diabetes medicine.
- If you’re already pregnant and you have diabetes, see your doctor right away.




Thank you for sharing the useful blog, Really very informative post.