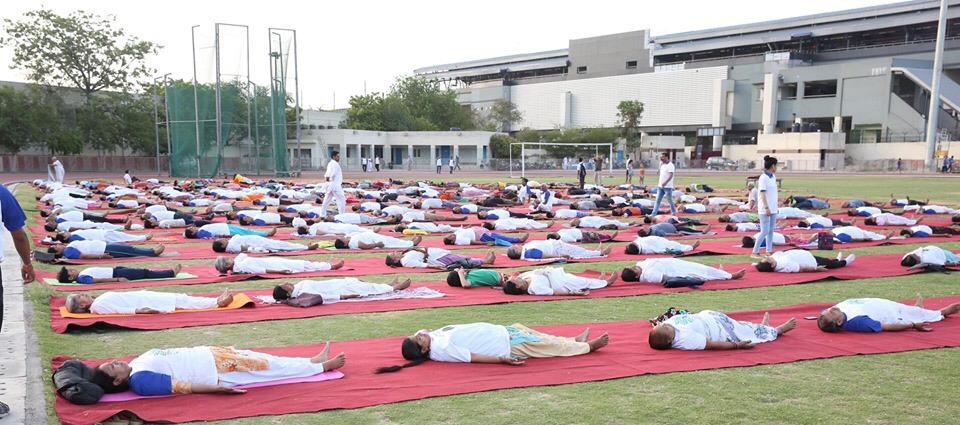

Tobacco smoking
Smoking has become fashionable these days. Over one billion people across the world are taking drugs in the form of tobacco. A large section, from teenagers to aged people, is taking this recreational drug, undermining its ill impact on health. The most common substance used in smoking is tobacco, while cannabis, opium, and heroin are also used as rare drugs. The primary important smoking method is through cigarettes, yet pipes, cigars, bidis, hookahs, vaporisers, and bongs are also used on a large scale. All the cigarette packets have a standard line, “Cigarette smoking is injurious to health”, yet the number of smokers increases daily. Smoking cigarettes causes death ten years later.
Smoking causes
There are many reasons for smoking. Some of the essential causes of smoking are given below
- Easing the feeling of anxiety
- People smoke on being upset or angry.
- Restless
- Experiencing pseudo relaxation
- Socialization with other smokers
- Feeling depressed
- During taking alcohol like beer, wine, and liquor
- During leisure time or whenever one feels aloof.
- To celebrate something
- While driving a car
- While thinking about some difficult situations
- While taking beverages like tea, coffee, etc.
- People also get fascinated by it after sex and meal
How to quit smoking with the help of Yoga?
There are many ways to quit smoking. But here, we will explain how yoga helps with smoking cessation. Regular yoga, comprising Suksha Vyayam, Asanas, Pranayama, and Mediation, helps to quit smoking. However, in yoga Nidra, the critical components play a vital role in smoke-free life.
Yoga is a spiritual heritage. Yoga is the science and art of healthy living. As a spiritual discipline, its purpose is inner transformation. For inner transformation, the field of Yoga emphasises the purification of mind, body, and soul. Thus, purification of the body through psychological and mental therapy is one of yoga’s most significant achievements. According to yogic philosophy, the mind is the most critical component in the cause of disease. One should be fit socially, physically, emotionally, mentally, culturally, and spiritually to be healthy. To know all these dimensions well, one should know the psycho-physiological mechanism of the body-mind and soul complex.
Yoga Nidra is an integral part of Yoga. Yoga Nidra is concerned mainly with Pratyahara (withdrawing senses from sense-objects) and Dharana (concentration). Yoga Nidra is the amalgamation of yoga relaxation and meditation. It also comprises a particular form of Yogic exercise usually known as “Exercise without Movement”. The result is travelling deeply to a place of extraordinary rest and self-awareness. Yoga Nidra can be applied as both the primary therapeutic tool and as an adjunctive treatment for many acute and chronic physical and psychological disease conditions.
In recent times, Yoga Nidra has been the brainchild of Swami Satyananda Saraswati, based on principles like tantric, especially Nyasa. In Nyasa’s authentic traditional tantric practice, consciousness and energy are injected into body parts systematically using mantras. Nyasa is performed to protect the body during powerful tantric rituals that invoke vast powers from the deep unconscious.
Nyasa may inject defensive power into the body for healing, rejuvenation, and as preparation for higher meditative processes. When used scientifically, using rhythm helps to induce deep relaxation and stimulation of the brain along the sensory and motor cortex, as well as powerful principles for psychological growth.
Yoga Nidra enables the creation of introversion (pratyahara). Pratyahara induces deep relaxation starting in the gross physical body, followed by systematically moving awareness and peace to the more subtle levels of being. It means initially relaxing the physical body, breath, mind, and psyche. As each part rests, another part opens up to our awareness, liberating energy that may have been trapped and connecting us to our dormant abilities and strength.
The process deepens our awareness of parts of ourselves that we usually cannot access because of tensions. Tensions block attention and energy. Deep relaxation liberates tensions from each layer, releasing power for healing and positive growth. It also unveils deeper layers of being and allows our inner potential to unfold, to be revealed and realised.
A recent study has shown that smokers are more extroverted, tense, anxious, depressive, and impulsive than non-smokers or ex-smokers. In Yoga Nidra, the consciousness directs the unconscious to relax. Yoga Nidra is a ‘sleep’ where all the burdens, stress, strain, and anxiety are thrown off to attain a more blissful state of awareness, a relaxation much more intense than ordinary sleep.
What is yoga Nidra (yogi sleep)?
Yoga Nidra consists of two words: yoga means ‘union’, and Nidra means ‘sleep’. We can say it is a ‘Yogic Sleep’ in a simplified form. Yoga sleep is also known as psychic sleep, which comprises a half-sleep and half-waking state. It is a state of inner awareness and contact with the subconscious and higher consciousness. In Yoga Nidra, we can experience all the facets of the mind, all the nooks and crannies of the mind, without the constraints of the physical body.
Yoga Nidra Stages
Yoga Nidra is divided into the following stages.
Preparation: Yoga Nidra is performed by practising Shavasana by closing your eyes. The yogic features like stillness, comfortable posture, breathing, and listening to soothing sounds help to relax the body and mind.
Resolve or Sankalp: The secret of transformation to quit smoking: Yoga Nidra has the power of overall personality transformation. Each session of Yoga Nidra burns out our old habits to be born new. In Yoga Nidra, seeds of change are planted in Sankalpa, which you make for yourself during each practice. Sankalpa is a Sanskrit word which can be translated as resolve or resolution. It is the most potent method for reshaping your personality. When the body and mind are relaxed, the practitioner is instructed to answer according to their wish. The Sankalpa should be short, clear, and positive. Sankalpa should be mental with complete determination, conviction, and confidence.
Rotation of consciousness: In Yoga Nidra, the practitioner is instructed to remain aware, to listen to the instructions, and to move the mind very rapidly according to the instructions without making any physical movements. The rotation of awareness in yoga Nidra follows a definite sequence: right side of the body, beginning with the right-hand thumb and ending with the little toe of the right foot; left side of the body, from the left-hand thumb to the little toe of the left foot; back of the body, from the heels to the back of the head; and lastly the front of the body, from the forehead and individual facial features to the legs.
Breath awareness: In this case, one becomes aware of the breath by watching it in the nostrils, chest, and abdomen or the passage between the navel and the throat. The practitioner becomes aware of each incoming and outgoing breath by mentally counting them and visualising the breath, cleansing their lungs.
Opposite feelings and sensations: In this stage, the physical or emotional sensations are recalled, intensified, and experienced fully. Usually, this is practised with pairs of opposite feelings or sensations like heat and cold, heaviness and lightness, pain and pleasure, love and hate, and so on.
Visualisation: This is the final stage of yoga. Nidra relates to mental relaxation. Generally, such images and symbols are chosen for the universal significance of visualisation. In the visualisation setting, the awareness is taken to the dark space in front of the closed eyes, referred to as chidakasha in yogic terminology. The practitioner is then instructed to visualise objects, stories, or situations in the chidakasha.
Sankalpa: Once again, the resolve or Sankalpa is intently thought of or visualised. Repeat the affirmation mentally three times with total dedication, faith, optimism, feeling, and emphasis.
Ending the practice: Before completing the session of Yoga Nidra, slowly, the awareness is externalised by asking the practitioner to become aware of the external sounds, objects, and persons. They are asked to move the body parts slowly and to stretch the body.





Nice Post.